Tracking customer success metrics is the key to customer loyalty and happiness.
“Customer loyalty is the most powerful sales and marketing tool.” – Bill Price
Contributing to your customers’ success with your services isn’t only beneficial for your customers. It is also beneficial for your business since it eventually leads to loyalty.
Customer success metrics are used to determine what kind of customer experience you are delivering. You can place yourself as a customer-centered business and embrace a company-wide ideology of nurturing customer growth, but you still need to know if the product is having a practical, positive impact on a customer’s daily workflow.
The goal of customer success is to generate recurring revenue by creating customer lifetime value. This means constantly sustaining and educating the customer, fitting your business approach to their specific needs. With customer success metrics, you can measure whether your efforts are working or not.
1. Churn Rate
Customer churn is the percentage of your customers that leave your service over a given time period. Examples include:
- Cancellation of a subscription
- Closure of an account
- Non-renewal of a contract or service agreement
- Consumer decision to shop at another store/use another service provider
This is one of the customer success metrics that you should absolutely measure. Before you can figure out what your churn rate is, you need to decide how you’re going to quantify actions such as those above and agree on what defines customer attrition for your business. Once you’ve done this, you can hit the books and do the math.
How To Calculate Churn Rate
While the formula is simplistic, in practice, SaaS churn can be both difficult to measure and define.
To calculate your churn rate, divide churned customers over a period of time by the number of customers you had at the start of that period. While overly simplistic, this allows you to focus on churn by cohort and analyze the cause — instead of debating between overly complex methods to analyze churn.

Want to easily calculate your churn and play with your numbers? Let’s analyze your current situation against your projection and see where your numbers end up using this SaaS Churn Calculator.
2. Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)
It is the average amount of revenue per customer or revenue generated per account measured in a defined period of time usually in months or years. It is useful for the analysis of a company’s revenue generation and growth at a per-unit level that helps in classifying high and low revenue products.
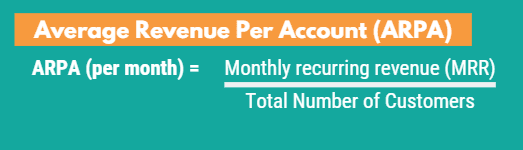
How To Calculate Average Revenue Per Account
Calculating ARPA involves dividing total revenue generated by all customers during a defined period by the number of customers. It is calculated using this simple formula:
3. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
A Net Promoter Score, or NPS®, simply asks whether someone is likely to recommend your company to someone else. The rep and their relationship with the customer plays a major role in this rating. Customer satisfaction is not only about the customers’ feelings towards the support representative or your product, but it is with their overall experience and how likely they are to return to your business.
The benefit of an NPS is that it provides both quantitative and qualitative data about your customers. Not only does it ask participants to rate their experience on a numeric scale, but it also asks them to provide an explanation for their score. That way, your business can analyze feedback based on the score, then examine the overall customer experience metrics if you come across abnormal or outlying results.
How To Measure Net Promoter Score
Measuring NPS is easier compared to other customer success metrics. You just need to ask your customers one question. “On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product or service?” Then, ask the participants to explain their score.
Customers that give a score of:
- 9 or 10 ratings are classified as promoters – They are enthusiastic guests who are happy with their stay.
- 7 to 8 ratings are passives – These guests are satisfied but could potentially stay at one of your competitors.
- 0 to 6 are Detractors – They are not particularly satisfied with their stay and most probably wouldn’t book again.
The NPS® is calculated by taking the percentage of promoters and subtracting the percentage of detractors. Depending on whether customers give low or high scores when asked if they would recommend a brand, the NPS® score can range from -100 to 100.
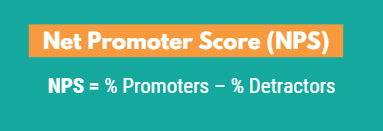
For example, if 68% of customers were promoters and 13% were detractors, then the brand’s NPS® would be positive (55). If on the other hand only 21% of customers were promoters and 57% were detractors, then the brand’s NPS® would be negative (-36).
4. Customer Retention Cost (CRC)
Customer Retention Cost is the total expenses a company typically commits in the form of technical support to keep and cultivate its existing customers. Calculating CRC involves the addition of all the costs necessary for customer retention and engagement.
CRC helps businesses invest in their customer success programs. While you may be excited to roll out new initiatives, you want to make sure that you’re spending your money in a cost-effective way. By measuring CRC, your business can make smart investment calls by comparing the potential cost of retaining customers versus the potential revenue you’ll generate from a new feature or service.
How To Calculate Customer Retention Cost
To calculate CRC, you’ll need to audit the expenses of all of your customer success efforts. This includes expenses spent on payroll for your customer success and service teams, engagement and adoption programs, professional services and training, and customer marketing. Once you add all of these expenses up into one sum, you can divide that value by your total number of customers to get your average customer retention cost.

5. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is a basic measurement of a customer’s satisfaction with a brand’s product and/or services. Marketers and brands can use CSAT to determine a customer’s level of satisfaction at key interaction times, such as the moment of purchase, the onboarding process, a support ticket exchange and a phone or digital conversation with customer service.
How To Calculate Customer Satisfaction Score
Like NPS, the customer satisfaction score requires a survey to measure it. But, you’ll need to trigger this survey after a customer interaction, so you can get the most accurate response from your participant. Remember, this is one of the customer success metrics where you should analyze the customer’s immediate reaction to individual experience, not their overall perception of your brand.

Once you have your form set up, you can calculate CSAT by dividing the number of positive scores (scores six to 10) by the total number of scores you captured. Then, if you multiply your result by 100, you’ll have the percentage of customers who are happy with their brand experience.
For example, if we received 50 responses and 40 of them were positive, then our CSAT would be 80% (40/50 = .80 x 100 = 80%).
This method of calculation is called the “top-2-box” measure of customer satisfaction because it only takes into account the two highest possible response ratings: “satisfied” and “very satisfied.” Studies have shown that the two highest values on customer feedback surveys are the most accurate at predicting customer retention.
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value is the metric that indicates the total revenue a business can reasonably expect from a single customer account. It considers a customer’s revenue value and compares that number to the company’s predicted customer lifespan. Businesses use this metric to identify significant customer segments that are the most valuable to the company.
Understanding the terms and conditions of a contract or service agreement plays a crucial role in accurately forecasting CLV, as these agreements outline the scope of services provided and the revenue expected from each customer.
Let’s face it. Acquiring new customers is far more difficult and expensive compared to increasing the revenue expected over the lifetime of an existing customer. Also, it is a reliable way of growth because CLV, if managed well can account for the majority of revenue coming from repeat purchases.
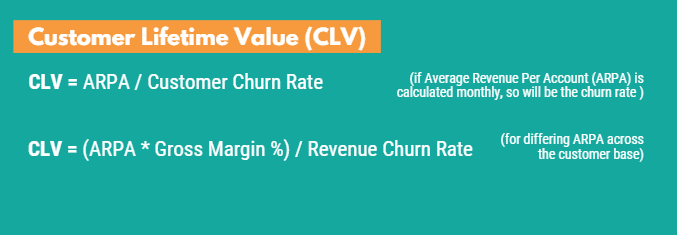
How To Calculate Customer Lifetime Value
CLV takes a customer’s revenue value and compares that number to the customer’s predicted lifespan. You can calculate CLV by multiplying your average purchase value by your average purchase frequency rate. Then take that value and multiply it by your average customer lifespan. This should leave you with the estimated amount of revenue that one customer will spend at your business.
CLV can be calculated using the formula:
7. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
MRR stands for monthly recurring revenue. It’s a normalized measure of a business’s predictable revenue that it expects to earn every month. For example, if you have 20 customers and they pay you $50 per month, your MRR would be $1,000.
It’s a great metric to use to determine how much your number of customers or their spending has grown since they started working with your business. You can keep track of their spending and compare this value over time to determine whether your consumers are succeeding with your products or not. This is particularly helpful for SaaS businesses that operate on a subscription model.
How To Calculate Monthly Recurring Revenue
To calculate monthly recurring revenue, you just need to multiply your total number of active customers by your average revenue per user. This should give you an idea of how much money you’re generating each month.
The basic formula for MRR is pretty simple: for any given month (period t), simply sum up the recurring revenue generated by that month’s customers to arrive at your MRR figure.

By calculating this, you would see how much your customers are actually spending on your offers. If you’re doing well, then you know that customers are not only enjoying your product or service but are thriving because of it.
Conclusion: Track these Customer Success Metrics
Metrics are everything. They give you a gauge to work against. These metrics uncover weaknesses and strengths. They can be your redemption or ultimate downfall when it comes time to prove the ROI of your efforts.
Each of these customer success metrics gives you a profound look into your strategy—customer views, internal operations, and the list go on. They’ll provide a vision that will allow you to drive improvement and track your progress along the way.
To keep track of these metrics, you can use interactive KPI dashboards. This way your team can stay aligned on the latest information and keep improving your customer success strategy.




